What Is An MBBS Degree?
The MBBS qualification is an undergraduate medical degree that usually spans between five to six years after having finished college / sixth form.
This degree is received by students in the UK and Commonwealth countries and is equivalent to an MD degree in the US.
Teaching styles may vary across different universities, some taking the traditional route, where you are taught the scientific content for the first few pre-clinical years before moving into a clinical setting, whilst other universities prefer to integrate classroom teaching and clinical environments from the start.
Regardless of the course style, all programmes focus on preparing students for general practice as a junior doctor before specialising in later years.
What Is An MD Degree?
An MD degree is a higher postgraduate research degree that typically takes several years of full-time study.
It is distinct from the MBBS degree or other undergraduate medical degrees that individuals obtain to become licensed medical practitioners.
In the UK, the MD degree is often pursued by students who have already completed the MBBS degree and wish to carry out further research into a specific medical field, combining research findings with clinical practice.
As the MD degree is generally a higher research degree, applicants often need to have a certain level of clinical experience before applying.
To be eligible, individuals typically need to have completed their Foundation Year 1 (F1) training after medical school, however, entrance requirements may vary.
Oxford University, for example, requires applicants to be at Speciality Training Year 1 (ST1) grade or above.
In the US, however, the MD programme is the primary medical qualification. It is commonly awarded in the following countries:
- The United States
- Canada
- Philippines
- Russia
Is MBBS Equal To MD?
The short answer is no.
In the UK, the MBBS degree is not equivalent to the MD degree. The MBBS is an undergraduate medical degree, whilst the MD is a postgraduate, clinical research-based degree. The differences between the two qualifications vary between countries. Some examples of the differences are listed below:
-
- The United Kingdom (UK)
- MBBS: In the UK, the MBBS is the primary medical qualification obtained after having completed your 5 or 6-year undergraduate medical course.
- MD: The MD is a higher research-based degree which students may pursue after obtaining the MBBS qualification and at least F1 training.
- The United States (US)
- MBBS: In the US, the MBBS is an extensive postgraduate program which is considered equivalent to the MD.
- MD: The MD, awarded after completing medical school, is the primary medical qualification in the US.
- India
- MBBS: Like in the UK, in India, the MBBS is an undergraduate degree awarded after completing medical education.
- MD: The MD is a postgraduate medical degree that can be undertaken after meeting certain requirements.
- Australia
- MBBS: In Australia, the MBBS was, until recently, the only medical degree offered. It is a professional degree, fully qualifying you to practice as a doctor.
- MD: Recently, there has been a switch from the MBBS to the MD at universities. The main difference is that the MD is a postgraduate degree, however, both MBBS and MD degrees fully qualify you to work as a doctor.
- The United Kingdom (UK)
MBBS vs MD: Main Differences
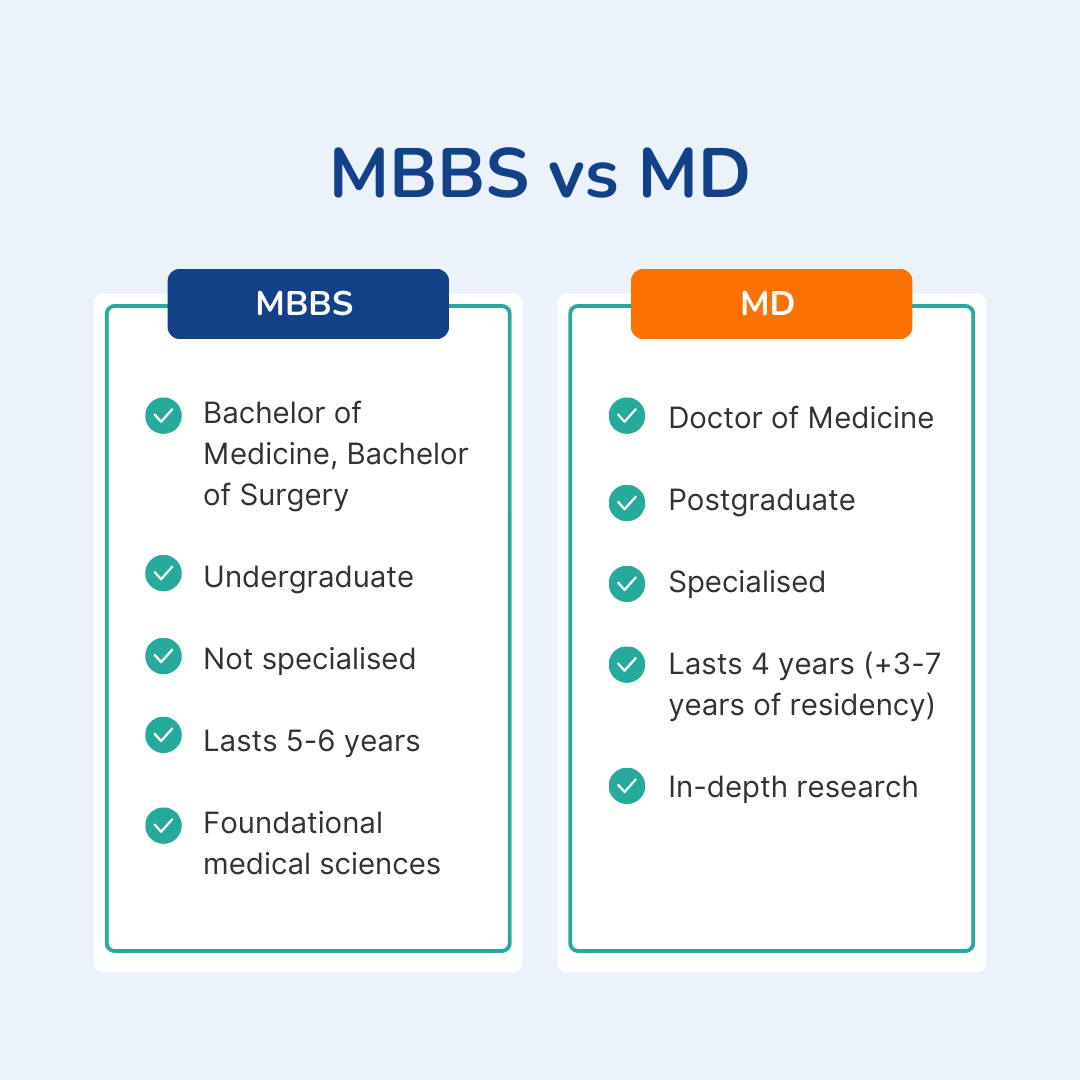
As discussed, MBBS and MD are two distinct qualifications in the UK. Their main differences lie in their levels of education and purpose within the medical education system. The key distinctions are listed below:
- Level of degree: The MBBS is an undergraduate degree. Its primary purpose is to provide the foundations for students to begin work as a junior doctor. The MD however, is a postgraduate, doctorate-level degree.
- Thesis vs dissertation: The MD is centred around in-depth research, where individuals are required to submit a thesis on their research findings. Some MBBS programs may require individuals to write a dissertation, but this is not a strict requirement.
- Pathway to MD: To embark on an MD, individuals need to have already obtained an MBBS or equivalent in their undergraduate degrees.
- Clinical Practice: Unlike the MBBS, in the UK the MD is not a clinical qualification on its own.
Duration: The MBBS program typically lasts between five to six years, whilst that of the MD program is typically four years – and includes a three-year residency (which could go up to seven years) at teaching universities and hospitals after graduation.
MBBS vs MD: Comparison
The general differences between the two qualifications are summarised in the table below.
| MBBS | MD | |
|---|---|---|
| Degree Type | Undergraduate degree | Postgraduate (doctorate) degree |
| Duration | 5 to 6 years | 4 years + a 3-7 year residency |
| Course Structure | Foundational medical sciences, clinical skills training, and practical rotations | In-depth research, may include some coursework on advanced medical topics, and the completion of a thesis |
| Speciality | No specialisation! It provides a general foundation for medical practice | Pursued by individuals looking to specialise in a specific medical field through research |
| Admission Requirements | Completion of college / sixth form with a focus on science subjects. Admission requirements vary depending on the university | Requires a primary medical qualification, often an MBBS. Admission is competitive and is based on academic achievements, research proposals, and often interviews |
| Course fees | Tuition fees vary by country and institution. In the UK, tuition fees for UK students are £9250 / year | Fees can vary significantly. Make sure you research your chosen institution’s fees before applying! |
Can You Become A Doctor If You Have An MBBS vs MD?
This varies depending on the country. Generally, obtaining either an MBBS or an MD qualifies an individual to become a doctor.
In many countries however, such as the UK, the MBBS serves as a primary qualification for those seeking to become doctors, whilst the MD on its own is not a clinical qualification.
The American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine offers a high-quality MD course. The curriculum is US-modelled, whilst the community is both supportive and friendly.
The course is aimed at current MBBS graduates who are seeking to become eligible for medical practice pathways in the US, UK and abroad.
Additionally, they offer three start dates in September, January, and May, giving you the freedom and flexibility to start the MD degree when it works for you!
If you are unsure about the MD degree, they offer a free on-demand webinar to learn more about the MBBS to MD pathway.
How to Choose Between MBBS vs MD?
Use the above guide to make sure you understand the differences between the two qualifications. Remember, these vary widely across different countries! A few key points you may want to think about are:
- In the UK, the MBBS (or an equivalent undergraduate course) must be done before the MD.
- The course structure for the two degrees is very different: the MBBS is focused on foundational medical sciences and translation of these into clinical practice, whilst the MD is very research-heavy, with students having to produce a thesis in order to complete the MD.
- The lengths of the programmes are very different. The MD is much more flexible and can be catered to your lifestyle and other commitments, whilst the MBBS is a full-time undergraduate course.
- Career aspirations can also greatly influence which path to choose. Completion of the MD is a great start into research, whilst the MBBS is much more clinically focussed.
Additional FAQs
Is MBBS Accepted In the US?
Yes, graduates of foreign medical schools, including those with an MBBS qualification, can apply for a certification to practice and may be eligible to pursue further training in the US.
Is MBBS Accepted in the UK?
Yes, the MBBS degree is widely accepted in the UK. Most doctors in the UK hold an MBBS or equivalent primary medical qualification.
Can I Pursue MD Before MBBS?
Typically, you must complete an undergraduate degree (for example the MBBS) before pursuing a postgraduate research degree such as the MD. This varies across countries: in the US, for example, the MD is the primary medical qualification.
How Long is MD After MBBS in the US?
In the US, the MD is the primary medical qualification and is earned after completing a medical school program (typically lasting four years.)